Modernism definition literature explores a pivotal interval in literary historical past. This period noticed a radical shift away from conventional types and themes, pushed by the tumultuous occasions of the early twentieth century. Authors experimented with new types and methods, reflecting the anxieties and transformations of their time. The evaluation will cowl key themes, authors, and methods of Modernism in literature.
This overview will delve into the core traits, analyzing the historic, philosophical, and societal influences on Modernist literature. It is going to additionally present examples and comparisons to grasp the evolution of literary actions. This in-depth exploration will assist readers admire the lasting influence of Modernism on modern writing.
Defining Modernism in Literature
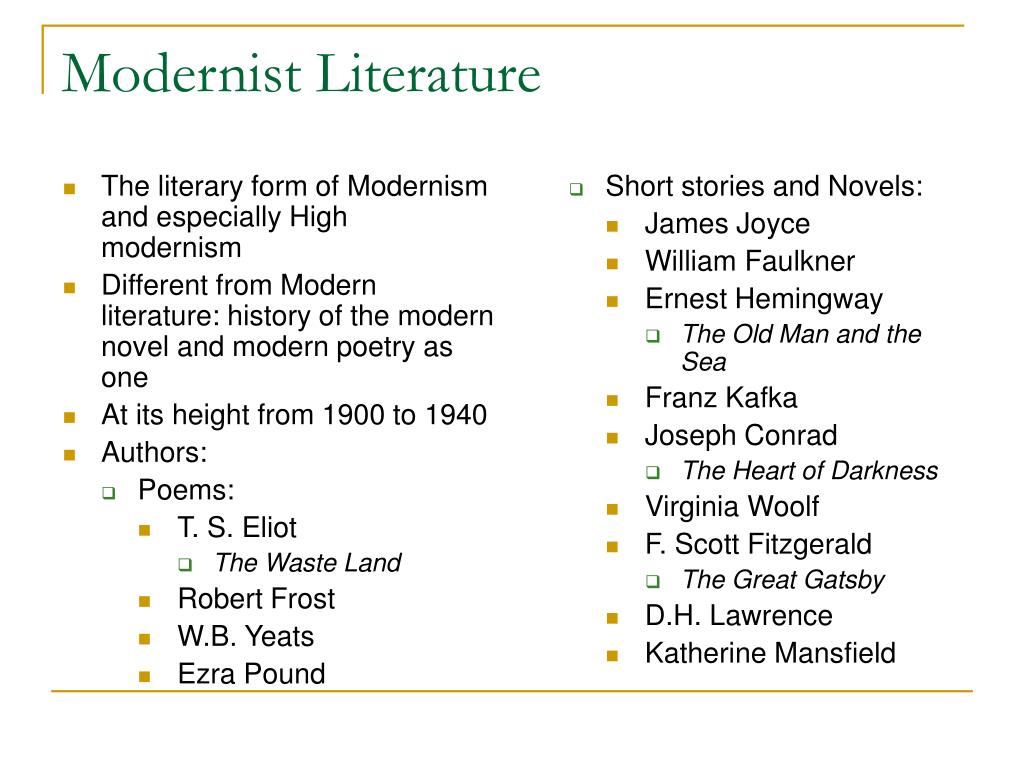
Modernism in literature, a major departure from conventional types and themes, emerged within the early twentieth century. It is a complicated and multifaceted motion characterised by a profound sense of disillusionment, experimentation, and a questioning of established norms. This era noticed a shift in how writers approached storytelling, pushing boundaries and reflecting the anxieties and uncertainties of the time.
Key Traits of Modernism
Modernist literature typically displays a way of alienation and fragmentation, stemming from the social and political upheavals of the period. Writers explored themes of disillusionment, loss, and the breakdown of conventional values. Key traits embody:
- Experimentation with type and elegance: Modernist writers rejected conventional narrative buildings, embracing stream of consciousness, fragmented narratives, and progressive poetic types. They sought to seize the complexities of human expertise, typically by means of subjective views and psychological depth. For instance, Virginia Woolf’s
-Mrs. Dalloway* makes use of inside monologue to painting the interior lives of its characters. - Exploration of psychological complexity: Modernist writers delved into the interior lives of their characters, revealing their ideas, emotions, and motivations. They used methods like stream of consciousness to painting the chaotic and infrequently contradictory nature of human expertise. James Joyce’s
-Ulysses* is a main instance of this, meticulously charting the ideas and emotions of its protagonist all through a single day. - Rejection of conventional values: The horrors of World Struggle I and different societal upheavals led to a profound disillusionment with conventional values and beliefs. Modernist writers typically explored the disillusionment and alienation skilled by people in a quickly altering world.
- Deal with subjective expertise: Modernist writers emphasised the significance of particular person notion and expertise. They challenged the notion of goal reality and as a substitute explored the subjective nature of actuality.
Historic Context of Modernism
The emergence of Modernism coincided with vital historic occasions, together with World Struggle I, the rise of industrialization, and the questioning of conventional social buildings. These occasions created a way of instability and uncertainty, prompting writers to mirror these anxieties of their work. The speedy adjustments of the early twentieth century created a profound sense of alienation for a lot of, and that is mirrored in modernist literature.
Philosophical and Mental Influences, Modernism definition literature
Modernist literature was considerably formed by varied philosophical and mental actions.
- Psychoanalysis: Sigmund Freud’s theories of the unconscious thoughts influenced Modernist writers’ exploration of the psychological complexities of their characters. That is evident within the works of writers like T.S. Eliot, whose poems grapple with the complexities of human consciousness.
- Existentialism: Existentialist philosophy emphasised particular person freedom and accountability in a seemingly meaningless universe. This philosophy resonated with many Modernist writers, who explored themes of alienation and the seek for which means in a world devoid of inherent function. Franz Kafka’s novels are a compelling instance of this.
- Nihilism: The devastating influence of World Struggle I fostered a way of disillusionment and a questioning of conventional values. Modernist writers typically explored the sense of meaninglessness and absurdity that characterised this period.
Comparability with Earlier Literary Actions
| Attribute | Romanticism | Realism | Modernism |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Emotion, creativeness, nature | Detailed depiction of on a regular basis life | Subjective expertise, fragmentation, alienation |
| Type | Lyrical, evocative | Goal, descriptive | Experimental, fragmented, progressive |
| Themes | Nature, individualism, heroism | Social points, realism, on a regular basis life | Disillusionment, alienation, loss |
This desk highlights the important thing variations between Modernism and its predecessors, demonstrating the numerous shift in literary focus and elegance.
Key Themes and Motifs
Modernist literature wasn’t nearly stylistic experimentation; it mirrored a profound shift in societal and philosophical views. The writers grappled with the aftermath of World Struggle I, the rise of industrialization, and the anxieties of a quickly altering world. These anxieties manifested in recurring themes and motifs that formed the very cloth of the style. They sought to seize the fragmented and infrequently unsettling realities of the fashionable expertise.
Recurring Themes
Modernist literature is characterised by a mess of recurring themes, stemming from the tumultuous instances during which it emerged. These themes typically explored the disillusionment and uncertainty of a world grappling with the implications of warfare and speedy societal change. The themes mirror a lack of religion in conventional values and buildings, a questioning of which means, and a way of alienation.
- Lack of Religion: Conventional non secular and societal buildings had been questioned and infrequently discovered wanting. The horrors of warfare and the altering social panorama shattered religion in established establishments, resulting in a way of disillusionment and ethical ambiguity. Writers explored the existential crises that arose from this loss, reflecting a profound questioning of which means in a seemingly meaningless world.
This lack of religion permeated many works, impacting characters’ actions and selections. For example, in T.S. Eliot’s “The Waste Land,” the decay of a civilization mirrors the lack of non secular and ethical route.
- Alienation and Fragmentation: The speedy tempo of industrialization and urbanization led to a way of isolation and detachment from group. Modernist writers typically depicted characters battling emotions of isolation and fragmentation, each on a person and societal stage. This alienation was mirrored in fractured narratives, fragmented consciousness, and characters’ struggles to attach with others or discover their place on the earth.
James Joyce’s stream-of-consciousness method exemplifies this fragmentation, showcasing the interior struggles of his characters.
- Experiences of Struggle: The trauma and disillusionment of World Struggle I profoundly influenced Modernist literature. Writers explored the psychological influence of warfare, portraying the bodily and emotional scars it left on people. The warfare’s brutal actuality challenged established notions of heroism and morality, resulting in a questioning of the very which means of existence. Erich Maria Remarque’s “All Quiet on the Western Entrance” powerfully captures the devastating results of warfare on the troopers’ psychological and emotional well-being.
- Modernity and its Discontents: The speedy tempo of change and the rise of industrialization created a way of unease and anxiousness. Modernist writers explored the challenges of adapting to a quickly reworking world, depicting characters grappling with the complexities of recent life. This theme is clear within the depiction of city landscapes, technological developments, and the altering social order.
Experimentation and Innovation
Modernist writers embraced experimentation in type and elegance, reflecting their need to seize the complexities of the fashionable world. They moved away from conventional narrative buildings and explored new methods to depict fragmented consciousness and subjective expertise.
- Stream of Consciousness: This system allowed writers to delve into the interior ideas and emotions of characters, capturing the fluidity and unpredictability of human consciousness. It typically concerned fragmented and nonlinear narratives, reflecting the fragmented nature of recent expertise. Virginia Woolf’s “Mrs. Dalloway” is a main instance of stream-of-consciousness, delving into the ideas and perceptions of its characters.
- Fragmentation and Discontinuity: Modernist writers typically used fragmented narratives and discontinuous buildings to mirror the fragmented nature of recent expertise. This system mirrored the disjointed and unsettling realities of the time, difficult conventional notions of linearity and coherence in storytelling.
- Objectivity and Impartiality: Modernist writers typically challenged conventional notions of objectivity and impartiality in storytelling. They sought to painting the world from a mess of views, reflecting the complexity and ambiguity of recent life. This method is usually seen in works that concentrate on the person’s perspective and the influence of societal adjustments on them.
Examples of Motifs
Modernist literature is replete with recurring motifs, every reflecting a specific facet of the anxieties and experiences of the time. These motifs typically reinforce the broader themes of the interval.
- Lack of Religion: The lack of religion in conventional values and establishments is usually mirrored within the characters’ ethical ambiguities and struggles to seek out which means in a seemingly meaningless world. The pervasive sense of disillusionment is a recurring motif in lots of modernist works. This lack of religion is usually expressed by means of disillusionment and existential questioning.
- The Disillusionment of Struggle: The horrors of warfare profoundly impacted the writers and their works. The brutality, the lack of life, and the shattered beliefs of warfare are sometimes mirrored within the characters’ trauma and psychological struggles. The motif of warfare’s devastating results permeates many modernist works, revealing the profound influence of battle on people and societies.
Manifestation in Completely different Authors
| Creator | Key Themes | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| T.S. Eliot | Lack of religion, fragmentation, disillusionment | “The Waste Land,” “The Love Music of J. Alfred Prufrock” |
| James Joyce | Fragmentation, stream of consciousness, alienation | “Ulysses,” “Dubliners” |
| Virginia Woolf | Stream of consciousness, psychological exploration, fragmentation | “Mrs. Dalloway,” “To the Lighthouse” |
| Franz Kafka | Alienation, absurdity, anxiousness | “The Metamorphosis,” “The Trial” |
Key Authors and Works
Modernist literature is a wealthy tapestry woven from the threads of experimentation and insurrection in opposition to conventional types. Key authors pushed boundaries, reflecting the anxieties and transformations of their time. Understanding their particular person contributions helps us admire the multifaceted nature of this literary motion.Modernist authors responded to a quickly altering world, grappling with the aftermath of warfare, industrialization, and social upheaval.
Their works typically explored themes of alienation, fragmentation, and the seek for which means in a seemingly chaotic world. This exploration led to progressive stylistic selections, difficult typical narrative buildings and poetic types.
Distinguished Modernist Authors and Their Works
A number of authors considerably formed the Modernist motion. Their particular person approaches and stylistic selections helped outline the interval.
- Virginia Woolf: A pivotal determine in Modernist fiction, Woolf is thought for her stream-of-consciousness method. Her novels, like Mrs. Dalloway and To the Lighthouse, present intimate portraits of interior lives and discover the complexities of human expertise. Woolf’s progressive method to time and narrative construction revolutionized the novel type.
- T.S. Eliot: A grasp of poetic experimentation, Eliot is famend for his exploration of the fragmented human psyche. His poem The Waste Land, a seminal work of Modernism, depicts a way of disillusionment and non secular vacancy. Eliot’s use of fragmented imagery and allusions is attribute of the period.
- James Joyce: A groundbreaking innovator, Joyce is praised for his groundbreaking use of stream-of-consciousness and experimentation with language. His novel Ulysses is a monumental work that explores the complexities of human consciousness and the challenges of recent life. Joyce’s progressive methods, comparable to inside monologue and symbolic imagery, pushed the boundaries of narrative construction.
- F. Scott Fitzgerald: Recognized for capturing the excesses and disillusionment of the Jazz Age, Fitzgerald’s novel The Nice Gatsby presents a poignant portrait of the American Dream’s elusive nature. Fitzgerald’s prose fashion and exploration of themes comparable to wealth, love, and social standing cemented his place in Modernist literature.
- Ernest Hemingway: Hemingway’s fashion is characterised by its concise prose and deal with motion and dialogue. His quick tales and novels, comparable to The Solar Additionally Rises and A Farewell to Arms, painting the disillusionment and psychological influence of warfare. Hemingway’s deal with objectivity and directness considerably impacted the fashion of subsequent writers.
Main Stylistic Traits of Virginia Woolf
Virginia Woolf’s distinctive fashion revolutionized the novel. Her progressive method to time, narrative construction, and characterization profoundly influenced subsequent writers.
- Stream of Consciousness: Woolf employed stream-of-consciousness, a method that mirrored the circulate of ideas and emotions in a personality’s thoughts. This allowed readers to expertise the interior world of her characters, delving into their subjective experiences.
- Inside Monologue: Her characters’ ideas, emotions, and recollections had been introduced in an uninterrupted and infrequently fragmented method, offering an intimate portrayal of their interior lives. Woolf’s use of inside monologue made her novels extremely immersive.
- Time and Reminiscence: Woolf challenged typical chronological buildings, blurring the strains between previous and current, and exploring how recollections formed the current. This system created a way of psychological depth in her narratives.
- Emphasis on Subjectivity: Woolf prioritized the subjective experiences of her characters, highlighting the significance of particular person views and perceptions.
Comparability of Woolf and Eliot
Virginia Woolf and T.S. Eliot, although each key figures, approached Modernism with distinct types. Woolf targeted on the interior lives of her characters, whereas Eliot explored the broader societal and cultural anxieties of the time.
- Woolf’s focus: Intimate, psychological explorations, stream-of-consciousness method, subjective views. Her novels provide intimate glimpses into the inside lives of her characters.
- Eliot’s focus: Broader social and cultural critique, fragmented imagery, poetic experimentation. His poems discover alienation, disillusionment, and the fragmentation of recent life.
Key Modernist Authors and Their Main Works
This desk summarizes the contributions of a few of the key figures in Modernism.
| Creator | Main Works | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Virginia Woolf | Mrs. Dalloway, To the Lighthouse | Exploring stream-of-consciousness and the complexities of human expertise. |
| T.S. Eliot | The Waste Land, The Love Music of J. Alfred Prufrock | Grasp of poetic experimentation, exploring themes of disillusionment and fragmentation. |
| James Joyce | Ulysses, Dubliners | Groundbreaking innovator of stream-of-consciousness and narrative methods. |
| F. Scott Fitzgerald | The Nice Gatsby | Capturing the excesses and disillusionment of the Jazz Age. |
| Ernest Hemingway | The Solar Additionally Rises, A Farewell to Arms | Recognized for concise prose and deal with motion and dialogue. |
Modernist Literary Methods
Modernist writers weren’t afraid to experiment with language and type to mirror the complexities of their time. They broke away from conventional storytelling methods, embracing new approaches that challenged readers and pushed the boundaries of literature. These progressive methods aimed to seize the fragmented and subjective expertise of the fashionable world.
Stream of Consciousness
Modernist writers typically sought to depict the interior workings of a personality’s thoughts, presenting ideas and emotions as they come up, relatively than by means of a conventional narrative construction. This system, referred to as stream of consciousness, creates a way of immediacy and authenticity. It permits readers to expertise the character’s subjective actuality, together with their random ideas, recollections, and associations. Virginia Woolf’sMrs.
Modernism in literature is principally about breaking the previous guidelines and experimenting with new types. Take into consideration how writers like Virginia Woolf challenged conventional storytelling. A latest controversy, just like the Julia Filippo leaks , exhibits how fashionable concepts about freedom and expression can even get actually messy and result in public scrutiny. Finally, modernism in literature is all about pushing boundaries and exploring new methods of telling tales.
Dalloway* is a main instance of stream of consciousness, vividly portraying the interior lives of varied characters as they navigate a single day.
Symbolism and Imagery
Modernist writers ceaselessly used symbolism and imagery to convey complicated concepts and feelings. They employed wealthy and evocative language to create highly effective and lasting impressions on the reader. That is typically a response to the disillusionment and anxieties of the time, permitting authors to discover the interior turmoil and chaos of the fashionable world by means of evocative imagery and symbolism.
T.S. Eliot’s
The Waste Land*, as an illustration, makes use of fragmented imagery and symbolism to depict the non secular and emotional desolation of post-war society.
Inside Monologue
Inside monologue is a key element of stream of consciousness, specializing in the presentation of a personality’s interior ideas and emotions. It is a essential method for exploring the psychological depths of characters and offering a window into their interior world. This system permits the reader to enter the thoughts of the character and expertise their ideas, emotions, and perceptions in a uncooked and quick manner.
Irony and Ambiguity
Modernist writers ceaselessly employed irony and ambiguity to mirror the uncertainty and complexity of the fashionable world. This system typically leaves the which means of a textual content open to interpretation, encouraging readers to have interaction actively with the fabric and assemble their very own understanding. This displays the dearth of clear-cut solutions and the seek for which means in a quickly altering world.
James Joyce’s
Ulysses* is a masterpiece of ambiguity, forcing readers to grapple with a number of layers of which means and interpretation.
Desk of Modernist Literary Methods
| Literary Approach | Rationalization | Instance |
|---|---|---|
| Stream of Consciousness | Presenting a personality’s ideas and emotions as they come up, with out a linear narrative construction. | Virginia Woolf’sMrs. Dalloway* |
| Symbolism and Imagery | Utilizing symbolic objects and vivid descriptions to convey complicated concepts and feelings. | T.S. Eliot’s
|
| Inside Monologue | Presenting a personality’s interior ideas and emotions immediately, typically inside a story. | James Joyce’s – Ulysses* |
| Irony and Ambiguity | Utilizing contradictory or unclear language to mirror the uncertainty of the fashionable world. | James Joyce’s
|
Modernism and Society

Modernist literature wasn’t born in a vacuum. It emerged from a world grappling with the devastating penalties of industrialization, the horrors of World Struggle I, and the speedy rise of recent applied sciences. Writers of this period reacted to those tumultuous instances with a profound sense of disillusionment and a need to discover the human situation in a radically altering world.
They sought to interrupt free from the constraints of conventional types and discover new methods of expressing the complexities of recent expertise.
Social and Political Context of Modernism
Modernism arose amidst vital social and political transformations. Industrialization introduced unprecedented wealth and technological development, but in addition widespread poverty, alienation, and a way of lack of conventional values. The rise of mass manufacturing and urbanization led to a breakdown of group buildings and a rising sense of anonymity. Political instability and battle, together with the rise of fascism and communism, additional fueled anxieties and formed the views of many writers.
Modernist Response to Social and Political Upheaval
Modernist writers did not merely observe these adjustments; they actively engaged with them. Their works typically mirrored a profound disillusionment with the established order and a questioning of conventional values. Many explored themes of alienation, fragmentation, and the lack of which means in a seemingly chaotic world. This typically manifested in fragmented narratives, stream-of-consciousness methods, and experimentation with type.
Influence of World Struggle I on Modernist Literature
World Struggle I used to be a watershed second that profoundly impacted Modernist literature. The unprecedented scale of dying and destruction, the mindless brutality of the battle, and the disillusionment with the warfare’s consequence left a long-lasting mark on writers. Many, like Erich Maria Remarque in “All Quiet on the Western Entrance,” depicted the horrors of warfare and the psychological trauma skilled by troopers.
The warfare challenged the idea in progress and purpose, inspiring a way of disillusionment and a questioning of societal norms.
Modernism and the Rise of Mass Media
The rise of mass media, together with newspapers, magazines, and radio, additionally performed a major position in shaping Modernist literature. Writers grappled with the ability of mass communication and its influence on particular person expertise and identification. The unfold of data and concepts additionally created new avenues for difficult established norms and creating a way of collective consciousness. Modernist writers typically explored the position of the person inside a mass society and the potential for each manipulation and empowerment by means of the media.
Socio-Political Elements Influencing Modernism
| Issue | Description | Instance |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Revolution | Fast industrialization led to urbanization, mass manufacturing, and social upheaval. | Elevated migration to cities, manufacturing facility work, and the rise of a brand new working class. |
| World Struggle I | Unprecedented scale of dying and destruction; challenged conventional values and beliefs. | “All Quiet on the Western Entrance,” the psychological trauma of warfare. |
| Rise of Mass Media | Newspapers, magazines, and radio; new methods of disseminating data and influencing public opinion. | Affect of propaganda and promoting on public notion. |
| Political Instability | Rise of fascism and communism, political unrest; created anxieties and social division. | The rise of totalitarian regimes and their influence on particular person freedoms. |
| Urbanization | Huge progress of cities, creating a way of anonymity and alienation. | The lack of group, the fragmentation of social life, and the expertise of isolation in city settings. |
Modernist Influences
Modernism wasn’t a vacuum; it sprung from a wealthy tapestry of mental and historic currents. Writers reacted to the speedy adjustments of their time, grappling with new concepts and experiences, and infrequently pushing again in opposition to conventional types and views. This exploration of various influences is essential to understanding the distinctive voice of Modernist literature.
Philosophical Influences
Modernist writers had been profoundly impacted by new philosophical actions, significantly existentialism. Existentialism emphasised particular person freedom and accountability in a seemingly meaningless universe. This philosophy resonated deeply with writers who witnessed the horrors of warfare and the breakdown of conventional societal buildings. Existentialist themes of angst, alienation, and the seek for which means permeated many modernist works.
Psychological Influences
Sigmund Freud’s theories of the unconscious thoughts revolutionized the way in which individuals understood human habits. Modernist writers integrated Freudian ideas, exploring the complexities of the human psyche, together with the position of unconscious wishes, anxieties, and repressed recollections. This deal with the interior world of the characters led to progressive literary methods like stream of consciousness, permitting for a extra nuanced portrayal of interior expertise.
Modernism in literature is all about breaking from conventional types, embracing experimentation, and reflecting the altering world. Take into consideration how writers like Virginia Woolf challenged the previous methods. Current occasions, just like the leaked paperwork from torialorraine here , are sometimes interpreted by means of a contemporary lens, showcasing how societal shifts are mirrored in literature. Finally, understanding modernism requires taking a look at how writers reply to main adjustments in society and tradition.
Scientific Developments
Fast scientific developments, significantly in physics and biology, challenged conventional notions of the world and human understanding. The speculation of relativity, for instance, fostered a way of uncertainty and instability, mirrored within the fragmented and disjointed narratives of modernist literature. The exploration of recent scientific discoveries contributed to a questioning of established norms and values.
Historic Influences
The influence of World Struggle I can’t be overstated. The unprecedented scale of destruction and loss, coupled with the disillusionment with conventional values, deeply affected modernist writers. They typically explored themes of disillusionment, trauma, and the lack of religion in progress. The warfare served as a catalyst for re-evaluating the human situation and the character of actuality.
Influence of Historic and Mental Influences
| Affect | Particular Contribution |
|---|---|
| Existentialism | Exploration of particular person freedom, accountability, and which means in a seemingly meaningless universe; themes of angst, alienation, and seek for which means. |
| Psychology (Freud) | Deal with the unconscious thoughts, unconscious wishes, anxieties, and repressed recollections; progressive literary methods like stream of consciousness. |
| Scientific Developments (e.g., Relativity) | Challenged conventional notions of the world and human understanding; sense of uncertainty and instability; questioning of established norms and values; fragmented and disjointed narratives. |
| World Struggle I | Disillusionment, trauma, and lack of religion in progress; exploration of themes of warfare, violence, and the human price of battle; re-evaluation of the human situation and nature of actuality. |
Modernism and the Way forward for Literature
Modernism, a literary revolution, did not simply disappear after its heyday. Its influence continues to resonate in modern literature, influencing types, themes, and approaches. Modernist methods and considerations proceed to be related, shaping how we write and browse at present.Modernist literature’s enduring legacy lies in its willingness to problem conventions and discover the complexities of the human expertise. This method has been adopted and tailored by subsequent generations of writers, making certain that Modernist beliefs stay potent forces within the literary world.
Enduring Influence on Subsequent Literary Actions
Modernism essentially altered the panorama of literature. Its emphasis on subjective expertise, fragmented narratives, and experimentation with type profoundly influenced the event of postmodernism and past. Postmodernist writers typically constructed upon modernist deconstructions of conventional narrative buildings, additional pushing the boundaries of what a narrative might be. The exploration of consciousness, evident in stream-of-consciousness methods, continues to fascinate and inform modern writers.
Enduring Relevance of Modernist Themes
Modernist writers tackled common themes like alienation, disillusionment, and the seek for which means in a quickly altering world. These themes stay profoundly related at present. The anxieties surrounding societal shifts, technological developments, and existential crises that permeated modernist works proceed to echo in modern considerations. Modernist literature’s deal with the human situation, stripped of romanticized notions, resonates with modern readers grappling with comparable points.
Enduring Legacy on Up to date Writing
Modernist methods, like stream of consciousness, inside monologue, and experimentation with type, proceed to encourage modern writers. Up to date authors typically draw inspiration from the modernist embrace of ambiguity and fragmentation. These methods enable writers to painting complicated characters and conditions in nuanced methods. A eager curiosity within the psychology of the person, evident in modernist works, nonetheless guides modern explorations of the human situation.
Examples of Up to date Writers Impressed by Modernist Methods
Up to date writers ceaselessly draw upon modernist methods. For example, Salman Rushdie’s experimental narratives and exploration of fragmented identities, or using metafiction within the work of Thomas Pynchon, showcase the lasting influence of modernist experimentation. Up to date poets typically make use of modernist methods to discover complicated feelings and views, as exemplified within the work of many modern poets.
The exploration of marginalized voices and experiences in modern fiction echoes the modernist concern for particular person experiences.
Checklist of Modernist Literary Works Nonetheless Studied Right now
Modernist works stay important parts of literary research. These works proceed to be appreciated and analyzed for his or her insightful portrayal of the human situation, technical innovation, and lasting relevance.
- James Joyce’s Ulysses: A landmark of modernist experimentation, its progressive narrative methods and exploration of consciousness proceed to fascinate readers and students.
- Virginia Woolf’s Mrs. Dalloway: A masterclass in stream-of-consciousness narration, exploring the complexities of interior life and social commentary.
- T.S. Eliot’s The Waste Land: A profound exploration of disillusionment and fragmentation, utilizing poetic methods to seize the anxieties of a post-war world.
- Franz Kafka’s The Metamorphosis: A chilling and surreal exploration of alienation and the absurdity of existence.
- Ernest Hemingway’s The Solar Additionally Rises: A poignant depiction of the misplaced technology’s struggles with which means and function, with a transparent and concise fashion.
Closure
In conclusion, modernism definition literature reveals a captivating interaction between societal upheaval, inventive innovation, and the enduring human expertise. From the fragmentation of conventional types to the exploration of complicated psychological states, Modernist writers captured the spirit of a transformative period. Their works proceed to resonate at present, inspiring and difficult readers to have interaction with the world round them.
FAQ Nook: Modernism Definition Literature
What’s the significance of stream of consciousness in Modernism?
Stream of consciousness allowed writers to depict the interior ideas and emotions of characters in a extra life like and complicated manner. It moved past conventional narrative buildings to signify the subjective expertise.
How did World Struggle I affect Modernist literature?
The horrors and disillusionment of World Struggle I profoundly impacted Modernist literature. Many writers explored themes of loss, trauma, and the breakdown of conventional values, reflecting the devastating results of the warfare on society.
What are some widespread themes in Modernist literature?
Widespread themes embody alienation, fragmentation, disillusionment, and the questioning of conventional values. These themes typically mirror the social and political anxieties of the period.
Who’re some key figures in Modernist literature?
Key figures embody T.S. Eliot, James Joyce, Virginia Woolf, and F. Scott Fitzgerald, every contributing considerably to the motion with distinctive types and views.
